Soft Skills for Product Designers
Introduction to Soft Skills in Product Design
While technical proficiency and design expertise are crucial, soft skills are equally essential for product designers. Soft skills encompass a range of interpersonal and cognitive abilities that enable designers to collaborate effectively, communicate ideas clearly, and navigate the complexities of the design process. These skills not only enhance individual performance but also contribute significantly to the success of design projects and the overall user experience.
Don Norman highlights the importance of these non-technical skills in his work:
"Designers must not only understand the technical aspects of creating products but also the human aspects of interacting with those products."
In this chapter, we will explore the key soft skills every product designer should cultivate, understand their impact on the design process, and provide actionable strategies to develop and enhance these abilities.
The Importance of Soft Skills in Product Design
Soft skills play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between technical design capabilities and the human-centric nature of product design. They facilitate effective collaboration, foster innovation, and ensure that designs resonate with users on a deeper level.
Enhanced Collaboration: Soft skills enable designers to work seamlessly with cross-functional teams, including developers, marketers, and stakeholders.
Effective Communication: Clear articulation of ideas and feedback ensures that design concepts are understood and implemented accurately.
Problem-Solving: Critical thinking and creativity drive innovative solutions to complex design challenges.
Adaptability: The ability to navigate changing project requirements and user needs ensures that designs remain relevant and effective.
Key Soft Skills for Product Designers
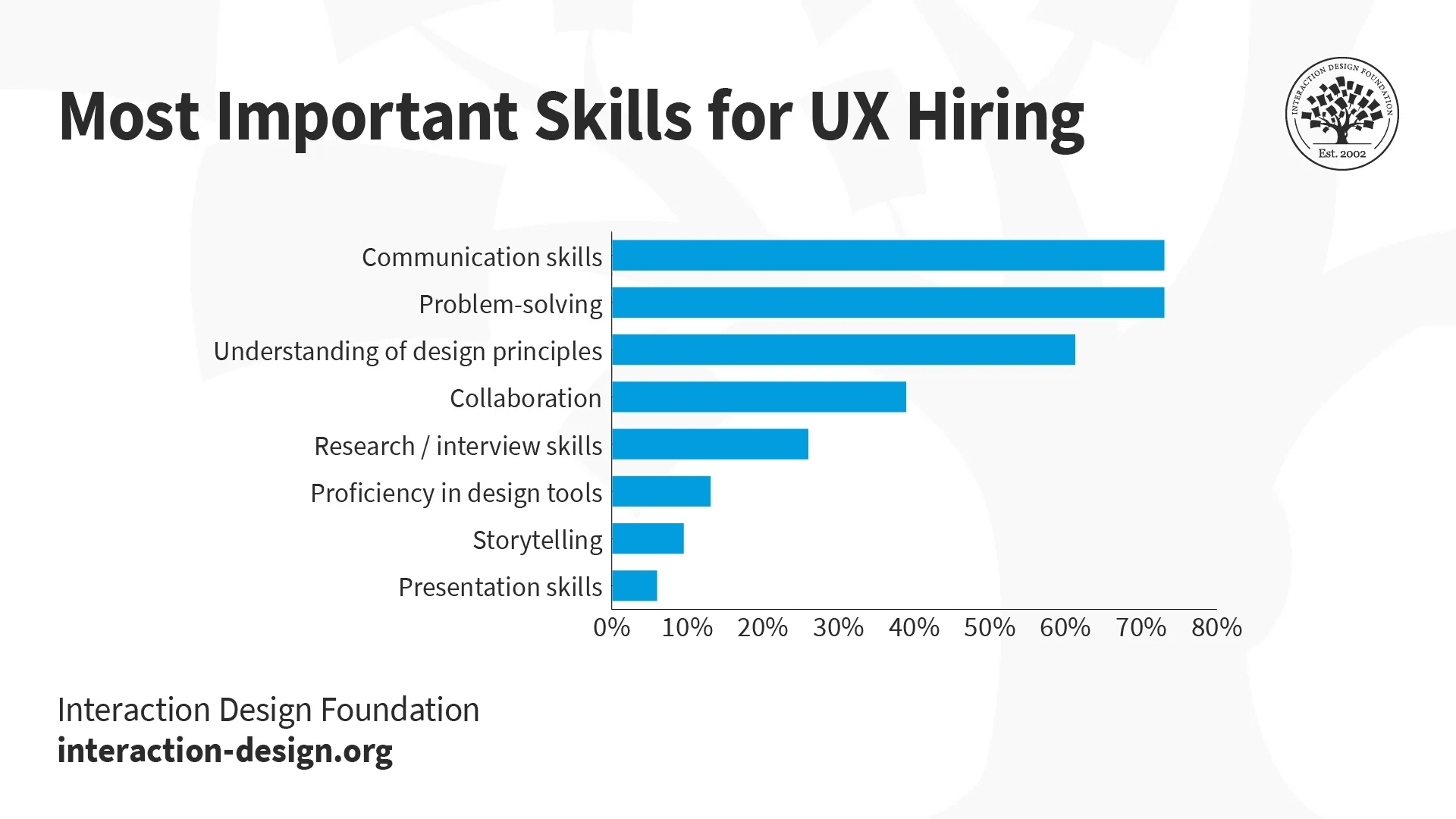
1. Communication
Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful product design. It involves not only conveying ideas clearly but also actively listening to feedback and understanding the perspectives of others.
Verbal Communication: Clearly presenting ideas, participating in discussions, and articulating design decisions.
Written Communication: Creating comprehensive documentation, writing clear briefs, and maintaining open channels of communication.
Visual Communication: Using visual aids like sketches, wireframes, and prototypes to illustrate concepts.
"Good communication is essential for effective design. Without it, even the best ideas can fail to take shape."
— Don Norman
2. Collaboration
Collaboration involves working effectively with others to achieve common goals. In product design, this means partnering with team members from various disciplines to create cohesive and user-centered products.
Teamwork: Contributing to group efforts, sharing ideas, and supporting colleagues.
Conflict Resolution: Addressing disagreements constructively to find mutually beneficial solutions.
Empathy: Understanding and valuing the contributions and viewpoints of others.
3. Empathy
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. For product designers, empathy drives user-centered design by ensuring that products meet real user needs and address genuine pain points.
User Research: Conducting interviews and observations to gain insights into user behaviors and motivations.
Persona Development: Creating detailed user personas to represent different segments of the target audience.
User Journey Mapping: Visualizing the user's experience to identify opportunities for improvement.
4. Problem-Solving
Problem-solving skills enable designers to navigate challenges and develop effective solutions. This involves critical thinking, creativity, and the ability to iterate on ideas based on feedback and testing.
Analytical Thinking: Breaking down complex problems into manageable components.
Creative Thinking: Generating innovative ideas and exploring unconventional solutions.
Iterative Design: Continuously refining designs based on testing and user feedback.
5. Adaptability
Adaptability is the capacity to adjust to new conditions and embrace change. In the fast-paced world of product design, being adaptable ensures that designers can respond to evolving project requirements and emerging trends.
Flexibility: Willingness to pivot strategies when necessary.
Continuous Learning: Staying updated with the latest design tools, methodologies, and industry trends.
Resilience: Maintaining composure and productivity in the face of setbacks or challenges.
6. Time Management
Time management involves organizing and planning how to divide your time between various tasks effectively. It ensures that designers can meet deadlines without compromising the quality of their work.
Prioritization: Identifying and focusing on the most important tasks.
Scheduling: Allocating specific time slots for different activities to maintain productivity.
Delegation: Assigning tasks to team members when appropriate to optimize workflow.
Developing and Enhancing Soft Skills
Cultivating soft skills requires intentional effort and practice. Here are actionable strategies to develop these essential abilities:
1. Practice Active Listening
Active listening involves fully concentrating, understanding, and responding thoughtfully to others. It enhances communication and fosters stronger collaborative relationships.
Techniques:
Maintain eye contact during conversations.
Avoid interrupting while others are speaking.
Reflect on what has been said before responding.
2. Seek Feedback and Reflect
Regularly seeking feedback from peers, mentors, and users provides valuable insights into your performance and areas for improvement.
Methods:
Conduct peer reviews of your work.
Participate in design critiques.
Use user feedback from testing sessions to inform your designs.
3. Engage in Team Activities
Participating in team-based projects and activities can enhance your collaboration and teamwork skills.
Suggestions:
Join cross-functional teams to gain diverse perspectives.
Participate in brainstorming sessions and workshops.
Take on leadership roles in group projects to develop coordination and management skills.
4. Develop Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence (EQ) is the ability to recognize, understand, and manage your own emotions and those of others. High EQ contributes to better teamwork and conflict resolution.
Strategies:
Practice self-awareness by reflecting on your emotions and reactions.
Develop empathy by putting yourself in others' shoes.
Manage stress through mindfulness and relaxation techniques.
5. Improve Presentation Skills
Being able to present your ideas confidently and clearly is vital for persuading stakeholders and collaborating with team members.
Tips:
Practice your presentations to build confidence.
Use visual aids effectively to support your points.
Engage your audience by encouraging questions and discussions.
Case Study: Enhancing Collaboration Through Soft Skills
![Image: Team of designers and developers collaborating on a project, emphasizing teamwork and communication.]
Background: A mid-sized tech company aims to improve its product development process by enhancing team collaboration and communication.
The Challenge
The company faced issues with miscommunication between designers and developers, leading to delays and inconsistencies in product features.
The Approach
Assessment of Soft Skills Gaps
Conducted surveys and interviews to identify areas where team members felt communication and collaboration could improve.
Training and Workshops
Organized workshops focused on effective communication, active listening, and conflict resolution.
Introduced team-building activities to foster trust and camaraderie.
Implementing Regular Check-ins
Established daily stand-up meetings to ensure everyone was aligned on project goals and progress.
Encouraged open feedback during design reviews and development sprints.
Promoting a Culture of Empathy
Initiated user empathy sessions where designers and developers discussed user personas and journey maps together.
Encouraged team members to share personal insights and challenges to build mutual understanding.
The Results
Improved Communication: Clearer and more effective interactions between designers and developers, reducing misunderstandings.
Enhanced Collaboration: Increased willingness to share ideas and support each other's work, leading to more cohesive product features.
Faster Iteration Cycles: Reduced delays and streamlined workflows, enabling quicker iterations and faster time-to-market.
Higher Team Morale: Strengthened team relationships and a more positive work environment.
Tools and Resources for Developing Soft Skills
1. Communication Tools
Slack: Facilitates real-time communication and collaboration among team members.
Zoom: Enables virtual meetings and presentations, enhancing remote communication.
Miro: Interactive whiteboard tool for collaborative brainstorming and planning.
2. Learning Platforms
Coursera: Offers courses on communication, leadership, and emotional intelligence.
LinkedIn Learning: Provides tutorials on teamwork, conflict resolution, and presentation skills.
Udemy: Features a variety of courses focused on personal development and soft skills enhancement.
3. Books and Literature
"Emotional Intelligence" by Daniel Goleman: Explores the importance of EQ in personal and professional settings.
"Crucial Conversations" by Kerry Patterson, Joseph Grenny, Ron McMillan, and Al Switzler: Provides strategies for effective communication in high-stakes situations.
"The Art of Possibility" by Rosamund Stone Zander and Benjamin Zander: Encourages creative thinking and collaboration.
4. Workshops and Seminars
Local Meetups: Participate in design and professional development meetups to practice soft skills in real-world settings.
Professional Conferences: Attend events focused on design thinking, leadership, and team collaboration.
Company-Sponsored Training: Engage in internal training programs that focus on enhancing soft skills within the workplace.
Actionable Steps to Enhance Your Soft Skills
Self-Assessment
Identify your strengths and areas for improvement in soft skills.
Use tools like personality assessments or seek feedback from peers to gain insights.
Set Specific Goals
Define clear, achievable objectives for developing each soft skill.
For example, aim to improve your public speaking by practicing presentations regularly.
Practice Regularly
Engage in activities that require the use of soft skills, such as leading meetings or participating in team projects.
Seek opportunities to apply and refine these skills in different contexts.
Seek Mentorship
Find mentors who excel in the soft skills you wish to develop.
Learn from their experiences and seek guidance on improving your abilities.
Reflect and Iterate
Regularly reflect on your interactions and identify what went well and what could be improved.
Adjust your approach based on these reflections to continuously enhance your soft skills.
Embrace Continuous Learning
Stay committed to personal development by continually seeking new learning opportunities.
Attend workshops, read relevant literature, and engage with communities focused on soft skill enhancement.
Applying Don Norman's Insights to Soft Skills
Don Norman's principles of user-centered design extend beyond technical skills, emphasizing the human aspects of design work. Here's how his insights can be applied to developing soft skills:
Empathy
Understanding Team Members: Just as empathy is crucial for understanding users, it is equally important for understanding and valuing the perspectives of your colleagues.
User-Centric Mindset: Maintain a focus on how your interactions and collaborations impact the overall design process and the final product.
Feedback
Constructive Criticism: Encourage and provide constructive feedback within your team to foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Open Communication: Create an environment where team members feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and feedback without fear of judgment.
Iteration
Continuous Improvement: Just as designs are iterated based on user feedback, soft skills should be continuously refined through practice and reflection.
Adaptability: Be willing to adjust your communication and collaboration styles based on the needs of different projects and team dynamics.
Problem-Solving
Collaborative Solutions: Use your problem-solving skills to address interpersonal challenges within the team, fostering a more harmonious and productive work environment.
Creative Thinking: Apply creativity not only to design problems but also to finding innovative ways to enhance team collaboration and communication.
Conclusion
Soft skills are an indispensable component of a successful product designer's toolkit. They enable designers to collaborate effectively, communicate clearly, and navigate the complexities of the design process with confidence and adaptability. By cultivating these skills, you enhance not only your personal effectiveness but also contribute to the overall success and innovation of your design projects.
Remember Don Norman's wisdom:
"Design is a process of constant discovery, learning, and iteration. A portfolio should reflect this journey."
Your ability to empathize, communicate, and collaborate will set you apart in the field of product design, enabling you to create products that truly resonate with users and stand out in the market.
Next Steps
In the next chapter, we will delve into User Research and Analysis, exploring advanced techniques for gathering and interpreting user data to inform your design decisions and create more effective, user-centered products.